Deactivating microglia reduces tau-linked brain damage in mice, study reveals
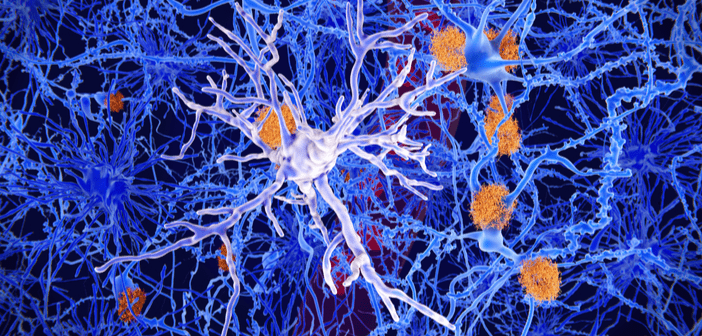
In a recently published study in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, researchers have revealed that microglia – which are activated as tau tangles accumulate in the brain – may form the crucial link between protein clumping and brain damage. Their findings suggest that eliminating microglia significantly reduces tau-linked brain damage in mice and implies that suppressing these cells could prevent or delay the onset of dementia. “Right now many people are trying to develop new therapies for Alzheimer’s disease, because the ones we have are simply not effective,” commented senior author, David Holtzman (Washington University School of Medicine, MO, USA)....