Stroke-like brain damage reduced by omega-3 acids in preclinical model
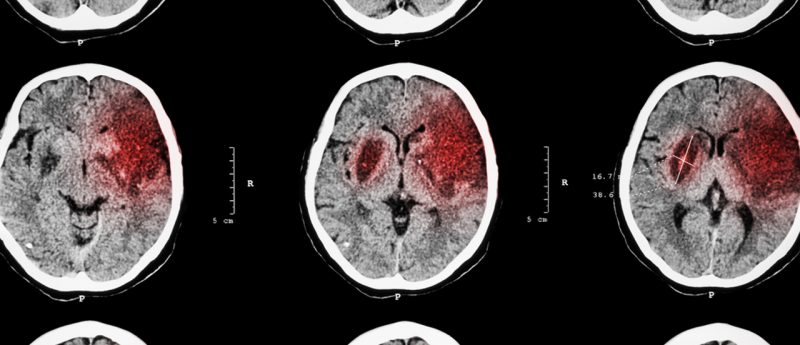
Researchers from Columbia University Medical Center (NY, USA) have treated a neonatal mouse model of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury utilizing triglyceride emulsions of docosahexaenoic acid (tri-DHA). Results indicate that treatment with tri-DHA may significantly reduce oxidative damage and improve neurological outcomes following these types of brain injury. The study, recently published in PLOS ONE, utilized the protective abilities of bioactive omega-3 fatty acids, as a potential treatment for stroke-like brain damage. Following the treatment, the 10-day old mice were evaluated for neurofunctional and neuropathological outcomes as well as oxidative injury after 24 hours and 8–9 weeks of recovery. At 24 hours,...