Tau accumulation in the brain may be linked to sleep apnea
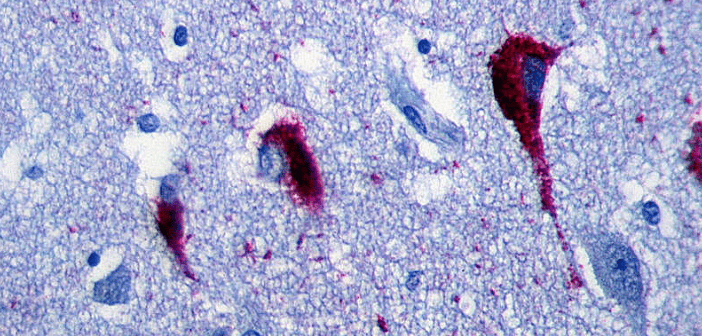
Researchers from the Mayo Clinic (MN, USA) have discovered that people who experience sleep apnea also present with higher levels of tau in their entorhinal cortex, compared to those who do not experience apneas. Lead author Diego Carvalho (Mayo Clinic) and colleagues have shown for the first time that people who experienced sleep apnea had on average 4.5% higher levels of tau protein in the entorhinal cortex than people who did not have apneas. The research will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 71st Annual Meeting (4–10 May, Philadelphia PA, USA). “A person normally has fewer than five...